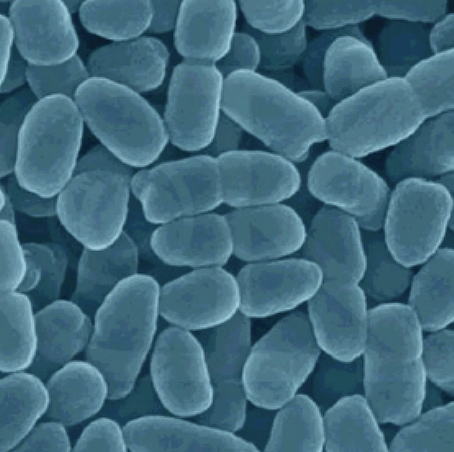
Bordetella Pertussis (B. pertussis) is a highly contagious gram-negative bacterium, which is transmitted by a cough, sneeze or simple exhalation. Due to a variety of secreted adherence factors and toxins, B. pertussis is highly adapted for nasopharyngeal colonization and is predisposed to evading host immunity. Pertussis toxin (PT), dermonecrotic toxin (DNT), and tracheal cytotoxin (TCT), are three pathogenic toxins that have been identified as playing key roles in the course of symptomatic whooping cough.